Lecture 5(b): IP Addressing
Conversion in Binary Form
IP Address in decimal form 192 . 168 . 30 . 24
First Octet 128 . 64 . 32 . 16 . 8 . 4 . 2 . 1
1 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 = 192
Second Octet 128 . 64 . 32 . 16 . 8 . 4 . 2 . 1
1 0 1 0 1 0 0 0 = 168
Third Octet 128 . 64 . 32 . 16 . 8 . 4 . 2 . 1
0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 = 30
Fourth Octet 128 . 64 . 32 . 16 . 8 . 4 . 2 . 1
0 0 0 1 1 0 0 0 = 24
Conversion in Decimal Form
IP Address in binary form 11001100 . 00011110 . 00111111 . 00011100
First Octet 128 . 64 . 32 . 16 . 8 . 4 . 2 . 1
1 1 0 0 1 1 0 0 = 204
Second Octet 128 . 64 . 32 . 16 . 8 . 4 . 2 . 1
0 0 0 1 1 1 1 0 = 30
Third Octet 128 . 64 . 32 . 16 . 8 . 4 . 2 . 1
0 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 = 63
Fourth Octet 128 . 64 . 32 . 16 . 8 . 4 . 2 . 1
0 0 0 1 1 1 0 0 = 28
Reference,very easy understanding
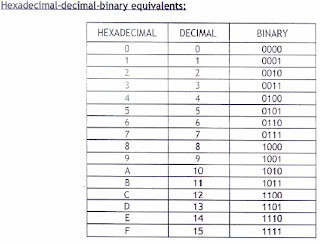
Conversion in Hexadecimal/Binary Form:
Network address :- Network address is a very first IP address of any network or subnetwork which can not be given to any host. If the network address is blocked whole network will be blocked because it represent the whole network.
You may say that it is a summary address of any network.
Example : 192.168.1.0 is a network address of 192.168.1.1 – 192.168.1.255
with default subnet mask.
By ANDing the Host address of 192.168.10.2 with 255.255.255.0
(its network mask) we obtain the network address of 192.168.10.0
Broadcast address :-
Broad cast address is very last IP address of any network and it is responsible for broadcasting. It also can not given to any host.
Example : 192.168.1.255 is a network address of 192.168.1.0 – 192.168.1.224
with default subnet mask.
In Next Lecture We will Start Subnetting.



Comments
Post a Comment