Lecture 7(a): Introduction to Routers
What is a Router?
Router is a device which makes communication possible between two or more different networks present in same or different geographical locations.
A router is a special type of computer. It has the same basic components as a standard desktop PC. However, routers are designed to perform some very specific functions. Just as computers need operating systems to run software applications, routers need the Internetwork Operating System software (IOS) to run configuration files. These configuration files contain the instructions and parameters that control the flow of traffic in and out of the routers.
Other Vendors apart from Cisco Many companies are manufacturing Router:
• Nortel
• Juniper
• Dlink
• Linksys
• 3Com etc.
Router Classification:
Router is a device which makes communication possible between two or more different networks present in same or different geographical locations.
A router is a special type of computer. It has the same basic components as a standard desktop PC. However, routers are designed to perform some very specific functions. Just as computers need operating systems to run software applications, routers need the Internetwork Operating System software (IOS) to run configuration files. These configuration files contain the instructions and parameters that control the flow of traffic in and out of the routers.
Other Vendors apart from Cisco Many companies are manufacturing Router:
• Nortel
• Juniper
• Dlink
• Linksys
• 3Com etc.
Router Classification:
1-FIXED ROUTER :
- (Non Upgradeable cannot add and remove the Ethernet or serial interfaces)
- Doesn’t have any slot
2-MODULAR ROUTER :
- (Upgradeable can add and remove interfaces as per the requirement)
- Number of slots available
- depend on the series of the router.
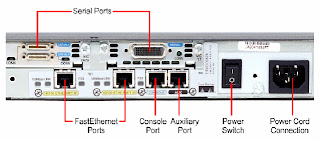
EXTERNAL PORTS(Interfaces) OF ROUTER:
1-WAN interfaces
1-WAN interfaces
- Serial interface (S0, S1 etc) – 60 pin/26 pin(smart serial)
- ISDN interface(BRI0 etc) – RJ45
2- LAN interfaces - Ethernet
- AUI (Attachment Unit Interface) (E0)15 pin
- 10baseT – RJ45
3-Administration interfaces(Configuration)
- Console – RJ45 – Local Administration
- Auxiliary – RJ45 – Remote Administration.
Internal Components of Router:
• ROM
A bootstrap program is located here. It is same as the BIOS of the PC. Bootstrap program current version is 11.0
• Flash
Internetwork Operating System (IOS) developed by Cisco is stored here. IOS is Command line interface.
• NVRAM
Non volatile RAM, similar to Hard Disk It is also known as Permanent Storage or Startup Configuration. Generally size of NVRAM is 32 KB.
• RAM
It is also known as Temporary Storage or running Configuration. Minimum size of RAM is 2MB. The size of RAM is greater than NVRAM in the Router.
• Processor
• ROM
A bootstrap program is located here. It is same as the BIOS of the PC. Bootstrap program current version is 11.0
• Flash
Internetwork Operating System (IOS) developed by Cisco is stored here. IOS is Command line interface.
• NVRAM
Non volatile RAM, similar to Hard Disk It is also known as Permanent Storage or Startup Configuration. Generally size of NVRAM is 32 KB.
• RAM
It is also known as Temporary Storage or running Configuration. Minimum size of RAM is 2MB. The size of RAM is greater than NVRAM in the Router.
• Processor
Motorola Processor 70 Mhz, RISC based processor (Reduced Instruction Set Computer)
Router Start-up(Boot up) Sequence:
• Bootstrap program loaded from ROM
• Bootstrap runs the POST
• Bootstrap locates IOS in Flash
• IOS is expanded and then loaded into RAM
• Once IOS is loaded into RAM, it looks for startup-config in NVRAM• If found, the configuration is loaded into RAM.
• Bootstrap program loaded from ROM
• Bootstrap runs the POST
• Bootstrap locates IOS in Flash
• IOS is expanded and then loaded into RAM
• Once IOS is loaded into RAM, it looks for startup-config in NVRAM• If found, the configuration is loaded into RAM.



Comments
Post a Comment